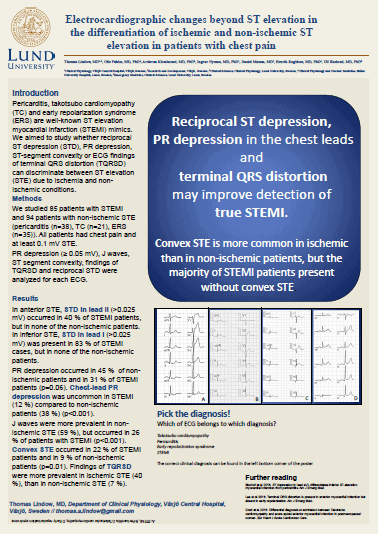
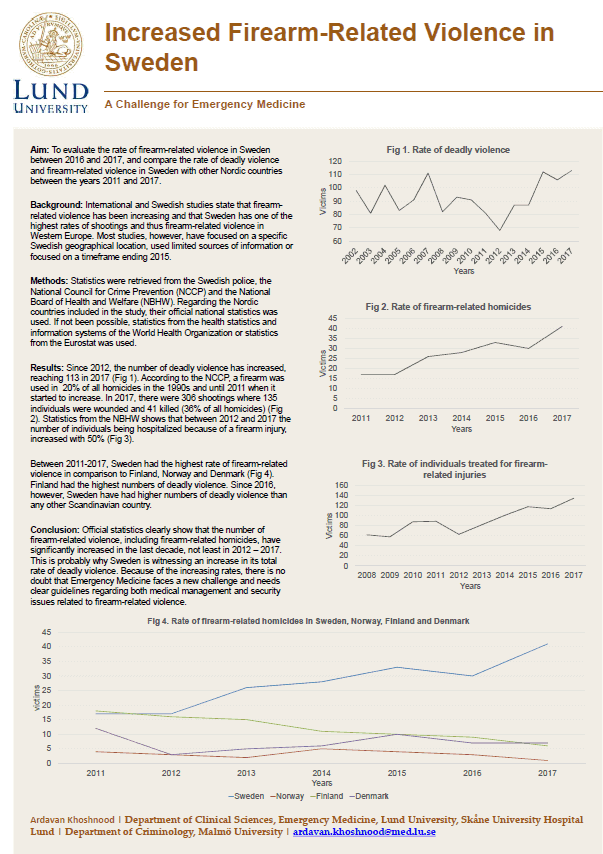
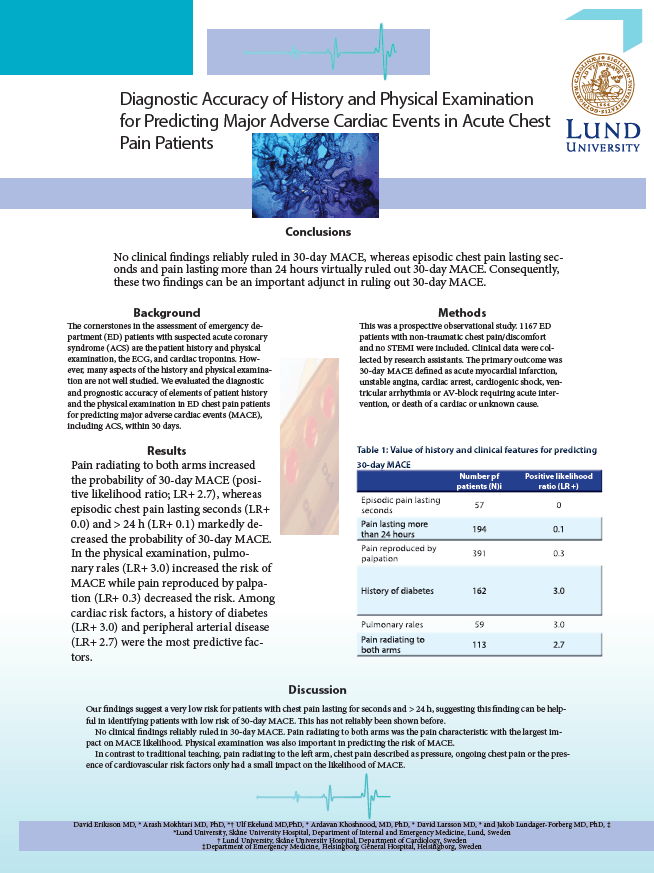
Deadly violence in Sweden: Profiling offenders through a latent class analysis
Background Sweden has in recent years witnessed increasing rates of firearm-related violence and homicide, which has contributed to increased rates of deadly violence. Attempts to profile offenders committing such crimes are of major importance, because such efforts may contribute to better preventive measures. We therefore aimed to study the characteristics of individuals convicted and/or suspected…


![Corona is a Threat to Sweden´s National Security [Swedish]](https://ardavan.se/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/logo-og.png)