A multicenter evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of a 0h/1h protocol in the assessment of emergency department chest pain patients
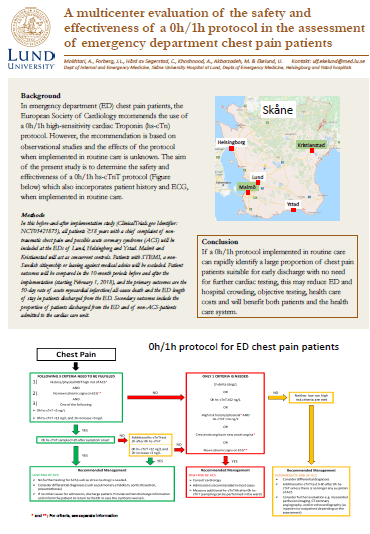
Background In emergency department (ED) chest pain patients, the European Society of Cardiology recommends the use of a 0h/1h high-sensitivity cardiac Troponin (hs-cTn) protocol. However, the recommendation is based on observational studies and the effects of the protocol when implemented in routine care is unknown. The aim of this study is to determine the safety…





![The ABC of Atrial Fibrillation at the Emergency Care Department [Swedish]](https://ardavan.se/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/LT4.jpg)